| Name: | Optical Coating |
| Substrate:: | Optical Glass/ Sapphire/ Infrared Optics |
| Coating:: | AR/ HF / Cut Off / Band Pass / DLC |
Product Description
.Optical Coating
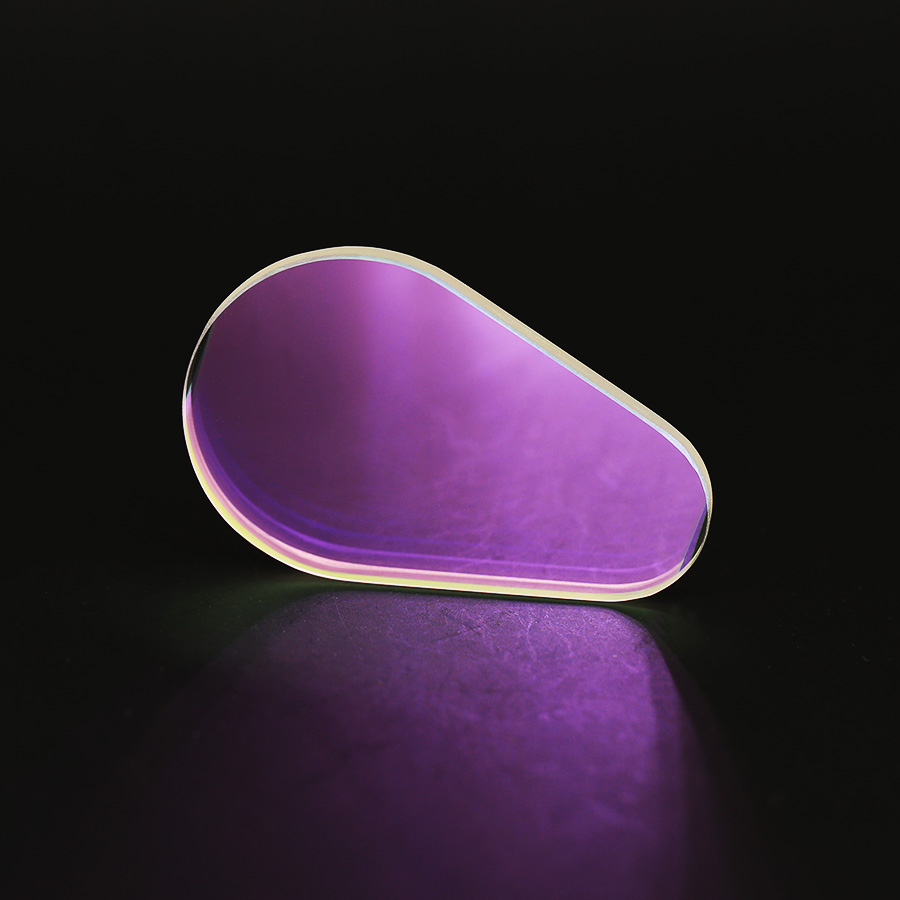
Optical coating refers to the process of coating a layer (or multiple layers) of metal (or dielectric) thin films on the surface of optical parts. The purpose of coating on the surface of optical parts is to reduce or increase light reflection, beam splitting, color separation, light filtering, polarization and other requirements. Commonly used coating methods include vacuum coating (a type of physical coating) and chemical coating.
Interference of light is widely used in thin film optics. In order to eliminate the reflection loss on the surface of optical parts and improve the imaging quality, one or more layers of transparent dielectric films are coated, which are called anti-reflection coatings. With the development of laser technology, there are different requirements for the reflectivity and transmittance of the coating layer, which promotes the development of multilayer high reflection coating and broadband anti-reflection coating. For various application needs, high reflective film is used to manufacture polarized reflective film, color spectroscopic film, cold light film and interference filter, etc. After the surface of optical parts is coated, the light is reflected and transmitted multiple times on the film layer to form multi-beam interference. By controlling the refractive index and thickness of the film layer, different intensity distributions can be obtained. This is the basic principle of interference coating.
.Coating Classification
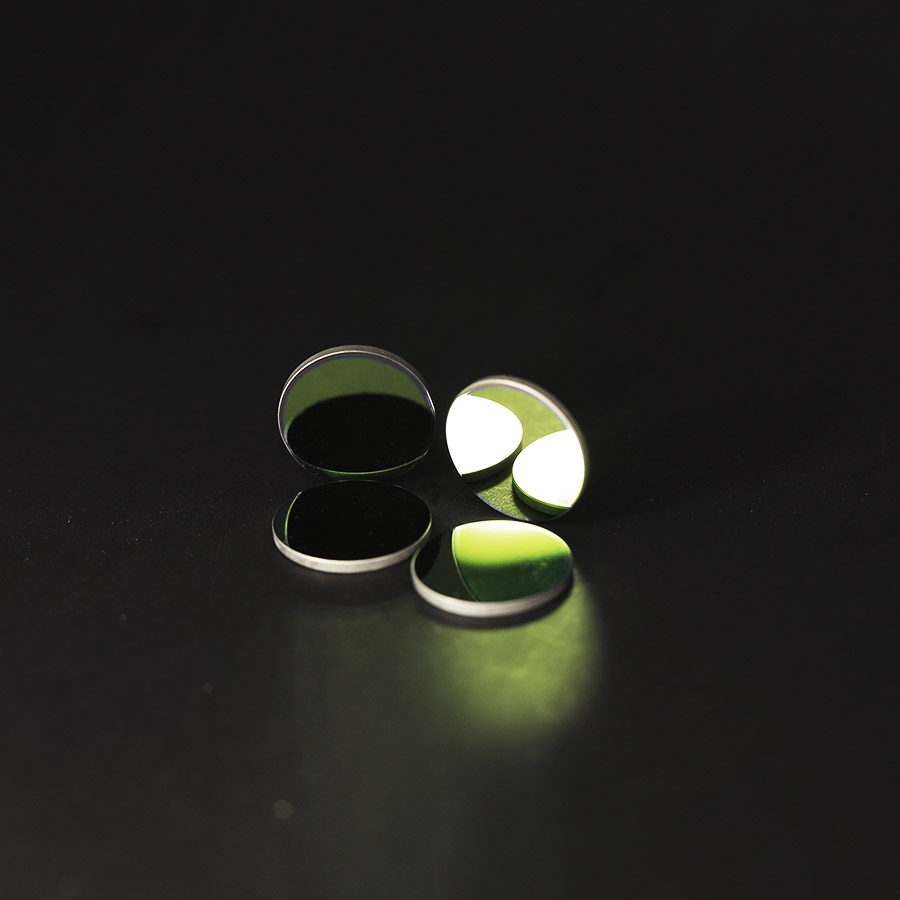
.Anti-reflection coating.
It is the most widely used optical film, which can reduce the reflectivity of the optical surface and increase its transmittance. For a single wavelength, the theoretical reflectance can be reduced to zero, and the transmittance is 100%; for the visible spectrum, the reflectance can be reduced to 0.5%, or even lower, to ensure that a complex system composed of multiple lenses has sufficient High transmittance and extremely low stray light. None of the modern optical devices are without anti-reflection treatment. Due to its extremely low reflectivity and bright surface color, glasses in modern people's daily life are generally coated with anti-reflection coatings.
.High reflection film
Can reflect most of the incident light energy back. When the dielectric film stack is selected, because the loss of the optical film is extremely low, as the number of film layers continues to increase, its reflectivity can continue to increase (close to 100%). Such highly reflective coatings are essential both in the manufacture of lasers and in laser applications.
.Energy splitting film
Part of the incident light energy can be transmitted, and the other part can be reflected and divided into two beams of light. The most commonly used is the splitting film with T:R=50:50.
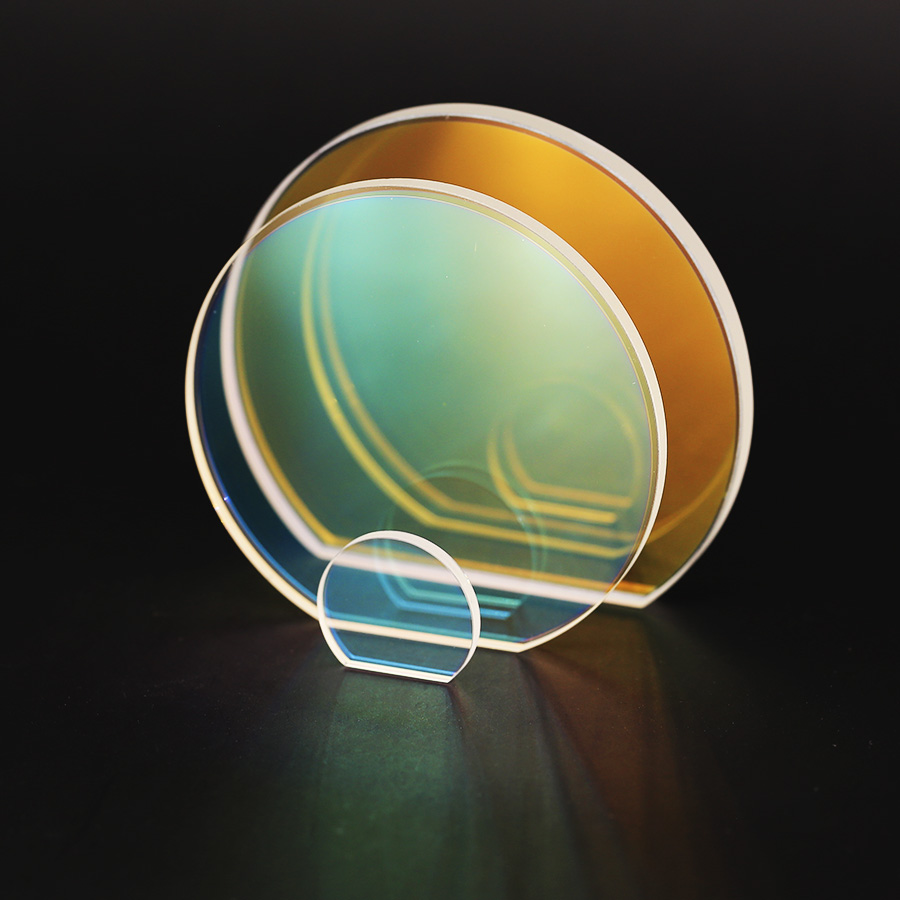
.Spectral splitting film
The energy of a part of the spectrum of the incident light can be transmitted, and the energy of another part of the spectrum can be reflected. The one that reflects long-wave energy and transmits short-wave energy is called short-wave cut-off filter film; the one that transmits long-wave energy and reflects short-wave energy is called long-wave pass cut-off filter film. They can be used to split a beam of light into multiple beams of different colors. For example, if a beam of light is divided into three primary colors of red, green, and blue, any color light can be obtained by combining these three colors. This color spectroscopic film is indispensable in the photoelectric color industry, such as color photography, color TV, color projection, color printing and other fields.
.Interference filter
An optical film that only passes light in a specific spectral range by using the principle of interference. Usually composed of multilayer films. There are many types of interference filters with different uses. Common interference filters are divided into cut-off filters and band-pass filters. The cut-off filter can divide the spectral range into two regions, the light in one region cannot pass through (cut-off region), while the light in the other region can fully pass through (pass-band region). Typical cut-off filters include short-pass filters (only allow short-wave light to pass) and long-pass filters (only allow long-wave light to pass), which are multilayer dielectric films with high refractive index layers and low refraction A periodic structure composed of alternating layers.
.Diamond-Like Carbon (DLC)
Referred to as DLC, has good optical transparency, wide optical bandwidth, especially in the infrared and microwave bands, and the optical refractive index is very high. Coating diamond-like carbon on infrared optical lenses The membrane can play the role of anti-reflection and protection.





Optic-Well Welcome You To Inquiry Us Any Time.










